Validation Model of Water Crisis Management Policy in Iran
Keywords:
model, crisis, policy-making, framework, water crisisAbstract
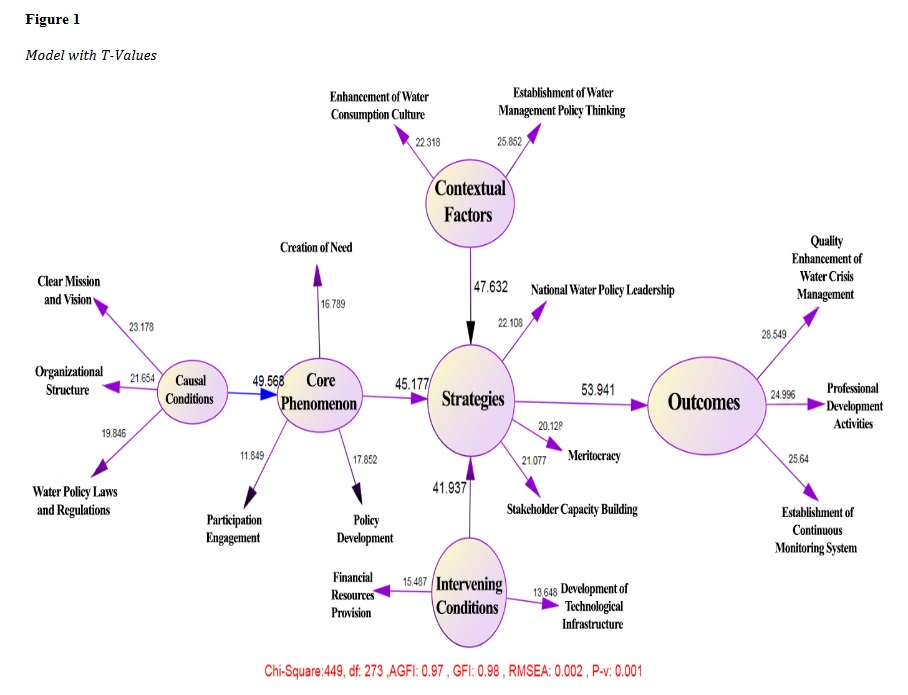
The present study is applied in nature and employs a quantitative, descriptive cross-sectional survey method for data collection. The statistical population comprises all experts and active managers associated with the water industry (national water resources management). According to the latest human resources statistics in national water resources management, the population includes 20,000 technical, engineering, and managerial personnel across the country. The sample size for this study was calculated using the Morgan table, resulting in a sample of 391 respondents. The research instrument consists of a 47-item questionnaire developed by Mahdavi Far et al. (2024). The reliability of the research instrument was assessed using Cronbach's alpha, yielding a value of 0.724. The findings from the study indicate that the highest path coefficient pertains to the relationship between strategies and outcomes, with a path coefficient of 0.947. The second highest is the relationship between causal conditions and the core category, with a path coefficient of 0.923. The relationship between contextual conditions and strategies follows, with a path coefficient of 0.879. The fourth highest path coefficient is between intervening conditions and strategies at 0.851, and finally, the core category and strategies have a path coefficient of 0.844. The results of the research demonstrate that causal conditions have a significant positive effect on the core phenomenon (β = 0.923, t = 49.568, p < 0.0001). Therefore, an increase in causal conditions leads to an increase in the core phenomenon. Additionally, contextual factors significantly and positively affect strategies (β = 0.879, t = 47.632, p < 0.001), suggesting that an increase in contextual factors leads to an enhancement in strategies. Intervening conditions also have a significant positive effect on strategies (β = 0.851, t = 41.937, p < 0.001), indicating that these conditions contribute to the reduction in strategies. Furthermore, the core phenomenon significantly and positively influences strategies (β = 0.844, t = 45.177, p < 0.001), suggesting that an increase in the core phenomenon enhances strategies. Finally, strategies significantly and positively affect outcomes or results (β = 0.947, t = 53.941, p < 0.001), indicating that an increase in strategies leads to improved outcomes or results.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Interdisciplinary Studies in Society, Law, and Politics

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.





