Understanding the Challenges of Language Barriers in Healthcare
Keywords:
Language barriers, healthcare, communication, patient safety, access to services, cultural competence, qualitative study, NVivo, interpreter services, healthcare deliveryAbstract
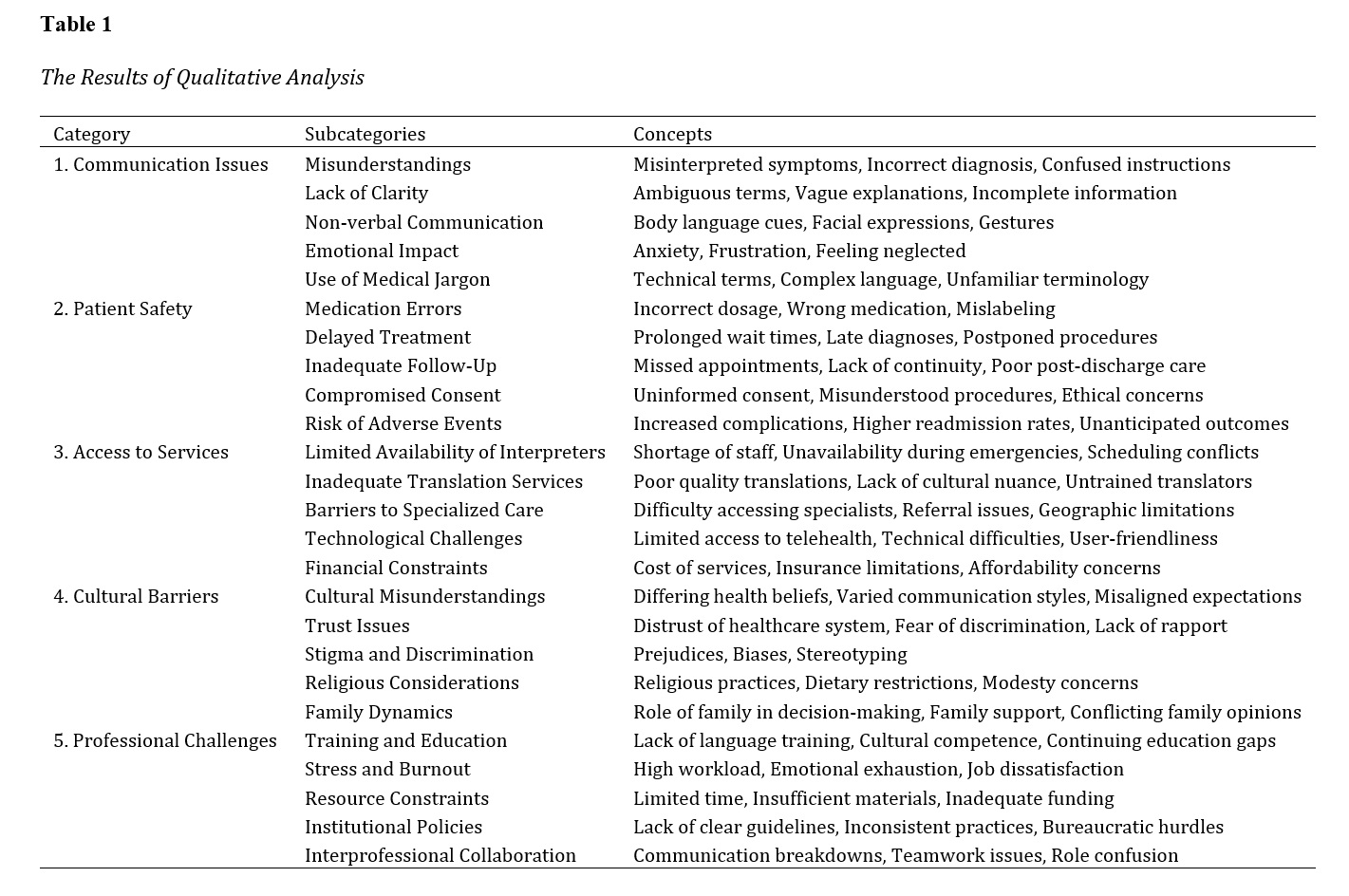
This study aims to explore the challenges posed by language barriers in healthcare settings, examining their impact on communication, patient safety, access to services, cultural understanding, and professional practices. The goal is to identify effective strategies for mitigating these barriers to improve healthcare delivery and outcomes for patients with limited language proficiency. This qualitative research employed semi-structured interviews to gather in-depth insights from 27 participants, including healthcare professionals and patients from diverse linguistic backgrounds. Data collection continued until theoretical saturation was reached. The interviews were transcribed and analyzed using NVivo software, following a thematic analysis approach. Key themes and subthemes were identified to understand the multifaceted challenges of language barriers in healthcare. Thematic analysis revealed five primary themes: communication issues, patient safety concerns, access to services, cultural barriers, and professional challenges. Language barriers led to frequent misunderstandings, incorrect diagnoses, and treatment errors. Patient safety was compromised due to medication errors and delayed treatments. Access to services was hindered by limited availability of interpreters and inadequate translation services. Cultural misunderstandings and trust issues further complicated healthcare interactions. Healthcare professionals faced stress and burnout due to inadequate training and resource constraints. These findings align with existing literature, emphasizing the pervasive impact of language barriers on healthcare delivery. Language barriers significantly affect healthcare quality and patient outcomes, necessitating comprehensive strategies to address these challenges. Effective interventions include investing in professional interpreter services, training healthcare providers in cultural competence, establishing clear institutional policies, and leveraging technology to improve communication. By implementing these strategies, healthcare systems can enhance patient safety, satisfaction, and access to care, ensuring equitable healthcare for patients with limited language proficiency.
Downloads