Youth, Politics, and Cyberspace: The Impact of Virtual Spaces on Partisan Tendencies and Political Attitudes in 1990s-born Iranians
Keywords:
Virtual spaces, political participation, youth, partisan activities, social media, political engagement, ANOVA, digital platformsAbstract
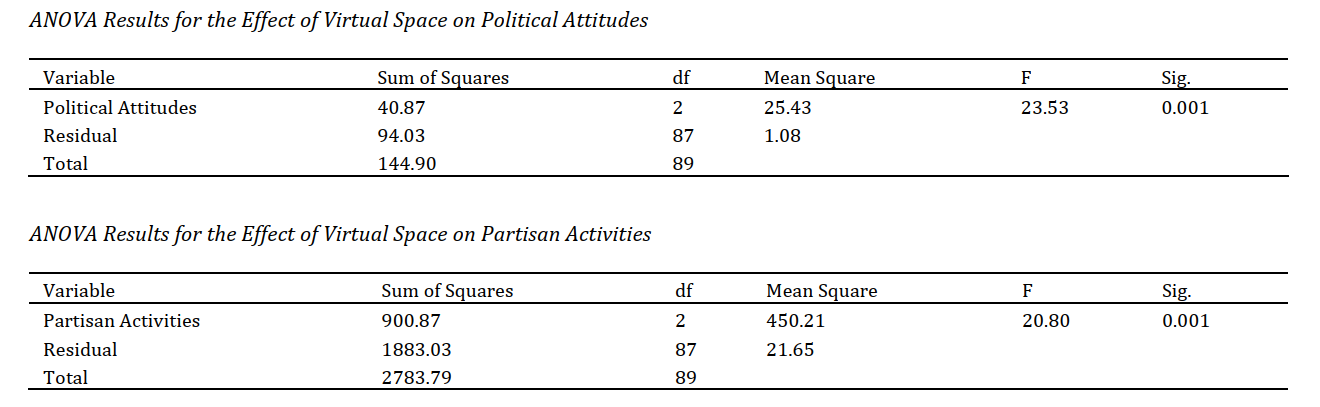
The expansion of virtual spaces has fundamentally transformed how individuals—especially youth—participate in political processes. This study focuses on how virtual spaces, particularly social media and online platforms, influence the political attitudes and partisan engagement of Iranian youth born in the 1990s (Gregorian calendar: 1991–2000). This study employed a quantitative research design and utilized Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) for evaluation. Data were collected from a sample of 1990s-born youth, and the study hypotheses were tested accordingly. ANOVA was used to analyze mean differences in political attitude scores and partisan activity levels. ANOVA results indicate that virtual spaces have a statistically significant impact on political attitudes (F = 23.53, p < 0.001) and partisan activities (F = 20.80, p < 0.01) among youth born in the 1990s. The findings confirm that virtual spaces play a vital role in shaping the political perspectives and partisan engagement of young individuals. The substantial influence of virtual spaces demonstrates that they serve as essential tools for political expression and participation among the younger generation. However, alongside increased engagement, these spaces also pose challenges such as the potential spread of misinformation and the intensification of political polarization.
Downloads
References
Ahmad, S. (2020). Political behavior in virtual environment: Role of social media intensity, internet connectivity, and political affiliation in online political persuasion among university students. Journal of Human Behavior in the Social Environment. https://doi.org/10.1080/10911359.2019.1698485
Alavi, N. (2005). Web of Politics: The Internet's Impact on Iranian Political Discourse. Books on Iranian Politics. https://books.google.com/books/about/Web_of_Politics.html?id=1x_dDAAAQBAJ
Antonova, E. V. (2023). Political Values, Orientations and Ideals of Modern Youth and Their Reflection in Virtual Space. Гуманитарий. https://doi.org/10.15507/2078-9823.063.023.202303.336-348
Castells, M. (2012). Networks of Outrage and Hope: Social Movements in the Internet Age. Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof/9780199595693.001.0001
Elliott, T. A., & Earl, J. (2021). Talking with or Talking at Young Activists? Mediated Youth Engagement in Web-accessible Spaces. https://doi.org/10.1108/S0163-786X20210000045004
Gil de Zúñiga, H., & Diehl, T. (2021). Digital platforms significantly shape political behavior and engagement. Journal of Communication.
Graham, M., & Khosravi, S. (2002). Reordering Public and Private in Iranian Cyberspace: Identity, Politics, and Mobilization. https://doi.org/10.1080/10702890212204
Grishaeva, S. A., & Shamaev, P. (2022). Young people's political participation in the digital environment. Цифровая социология. https://doi.org/10.26425/2658-347X-2022-5-1-25-35
Howard, P. N. (2011). The Digital Origins of Dictatorship and Democracy: Information Technology and Political Islam. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511762684
Istyagina-Yeliseeva, E. A., Barijenikova, A. V., & Boldyreva, E. (2020). Involvement of Russian student youth in Internet communications as a factor in the formation of models of their socio-political activity. Digital Sociology. https://doi.org/10.26425/2658-347X-2020-3-3-12-20
Kligler-Vilenchik, N., & Literat, I. (2017). Formative Events, Networked Spaces, And The Political Socialization Of Youth. In In: [Title of Edited Volume]. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315202129-8
Loader, B., Vromen, A., & Xenos, M. (2020). Virtual spaces mobilize youth for political activism. New Media & Society, 22(2), 227-244. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444820922363
Nacif, L. P. M. (2021). Social media and Iran - A Messy Relationship? https://www.internetjustsociety.org/social-media-and-iran-a-messy-relationship
Rahbarqazi, M., & Nourbakhsh, S. (2023). The Effect of Social Media on Iranian Citizens' Electoral Participation and Political Action. Communication & Society. https://doi.org/10.15581/003.36.2.83-95
Rahimi, B. (2003). Cyberdissent: The Internet in Revolutionary Iran. Middle East Review of International Affairs, 7(3), 101-115.
Rheingans, R., & Hollands, R. (2013). There is no alternative?': challenging dominant understandings of youth politics in late modernity through a case study of the 2010 UK student occupation movement. Journal of Youth Studies. https://doi.org/10.1080/13676261.2012.733811
Salamatian, L., Douzet, F., Limonier, K., & Salamatian, K. (2019). The geopolitics behind the routes data travels: a case study of Iran.
Saud, M., Ida, R., Mashud, M., Yousaf, F. N., & Ashfaq, A. (2023). Cultural dynamics of digital space: Democracy, civic engagement and youth participation in virtual spheres. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 97, 101904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijintrel.2023.101904
Shakhsari, S. (2012). From Homoerotics of Exile to Homopolitics of Diaspora: Cyberspace, the War on Terror, and the Hypervisible Iranian Queer. Journal of Middle East Women's Studies, 8(3), 14-35. https://doi.org/10.2979/jmiddeastwomstud.8.3.14
Theocharis, Y. (2020). Youth bypass traditional structures but still engage in political participation via virtual platforms. In In: [Title of Edited Volume].
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Shahin Golafshannia, Mohammad Ali Khosravi, Seyed Ali Mortazaviyan, Ahmad Bakhshaishi Ardestani (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.





